|
|
Managers, executives and directorsМинистерство образования и науки республики Казахстан Таразский государственный университет им. М.Х. Дулати Кафедра иностранных языков
Учебно-методическое пособие к дисциплине «Профессионально – ориентированный иностранный язык» Для экономических специальностей: финансы, УиА, экономика, менеджмент.
Составители: Ким И.А. Кантаева Г.Г. Рахимова Ю.С.
Тараз 2016 Content
Unit I Company structure Lead-in • Which department - production, finance, accounting, marketing, sales, human resources, etc. - of an organization do you think is the most interesting to work in? • Is it better to have one immediate boss or to work for more than one manager? • Do you prefer to work alone or in a team? • Is it more motivating to be responsible to someone for your work, or responsible for people who report to you? Vocabulary Ex. 1 Match the departments with their responsibilities a - Human Resources b - Marketing c - Research and Development d - I.T. (Information Technology) e - Maintenance f - Sales g - Customer Service h - Finance i - Dispatch Department j - Production Department
Responsible for taking care of customer needs Responsible for selling the product/service Responsible for making the product Responsible for how a product/service is advertised and promoted Responsible for hiring new staff Responsible for the company's computers and network Responsible for the office/building Responsible for discovering new knowledge about the product, improving it and creating new products Responsible for payments, bills and expenses Responsible for the delivery of orders
Ex.2 Before reading about traditional company organization check your understanding of some basic terms by matching up the following words and definitions. ____________________________________________________________________________ to delegate to report to autonomous line authority function hierarchy or chain of command
1 ___________ a system of authority with different levels, one above the other, e.g. a series of management positions, whose holders can make decisions, or give orders and instructions. 2 ____________ a specific activity in a company, e.g. production, marketing, finance. 3 ___________ independent, able to take decisions without consulting someone at the same level or higher in the chain of command. 4 _______________ the power to give instructions to people at the level below in the chain of command 5 _______________ to be responsible to someone and to take instructions from them 6 _______________ to give someone else responsibility for doing something instead of you
Reading1 Company structure
Comprehension 1 What is the main advantage of a chain of command? 2 Why is it not usually possible to organize a large organization in a single hierarchy? 3 In what ways can dividing a business functionally cause problems? 4 What factors might lead companies to flatten their hierarchies? 5 According to the text, what kind of managers might not want to delegate decision making?
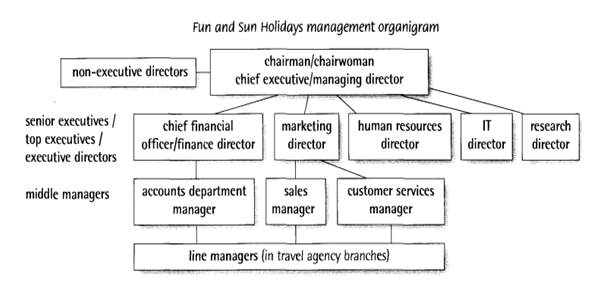
Reading 2 Managers, executives and directors Managers and executives in the UK
All the directors together are the board. They meet in the boardroom. Non-executive directors are not managers of the company; they are outsiders, often directors of other companies who have particular knowledge of the industry or of particular areas. The marketing director is the head of marketing; the IT director is the head of IT, etc. These people head or head up their departments. Informally, the head of an activity, a department or an organization is its boss. An executive or, informally, an exec, is usually a manager at quite a high level (for example, a senior executive). But 'executive' can be used in other contexts to suggest luxury, as in 'executive coach' and 'executive home', even for things that are not actually used by executives. Managers and executives: US
In the US, the top position may be that of chairman, chairwoman or president. This job is often combined with the position of chief executive officer or CEO. Some companies have a chief operating officer to take care of the day-to-day running of the company. The finance director may be called the chief financial officer. In the US, senior managers in charge of particular areas are often called vice presidents (VPs).
|
|