|
|
Competitive advantage refers to what sets the organization apart from others and provides it with a distinctive edge for meeting customer or client needs in the marketplaceHow can the organization adapt to or control such external elements as competitors, customers, government, and creditors in a fast-paced environment? What strategic and structural changes are needed to help the organization attain effectiveness? How can the organization avoid management ethical lapses that could threaten its viability? How can managers cope with the problems of large size and bureaucracy? What is the appropriate use of power and politics among managers? How should internal conflict be managed? What kind of corporate culture is needed to enhance rather than stifle innovation and change, and how can that culture be shaped by managers? Challenges for managers: Globalization Intense competition Rigorous ethical scrutiny The need for rapid response The digital workplace Increasing diversity Organizations: social entities that are goal-directed, designed as deliberately structured and coordinated activity systems, are linked to the external environment. Organizations exist in order to: Bring together resources to achieve desired goals and outcomes Produce goods and services efficiently Facilitate innovation Use modern manufacturing and information technologies Adapt to and influence a changing environment Create value for owners, customers, and employees Accommodate ongoing challenges of diversity, ethics, and the motivation and coordination of employees
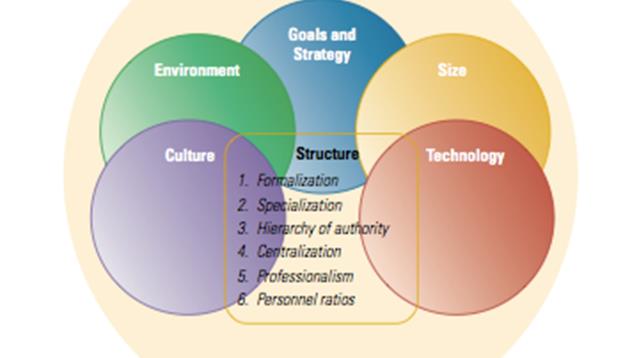
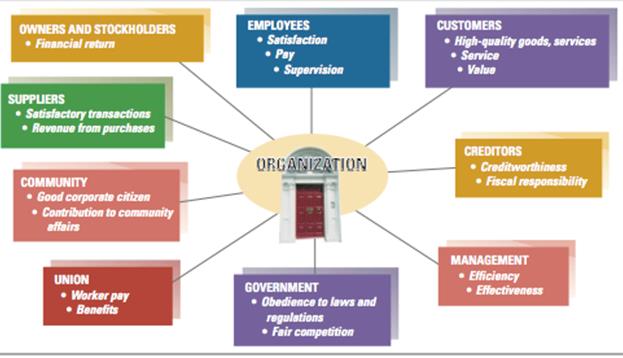
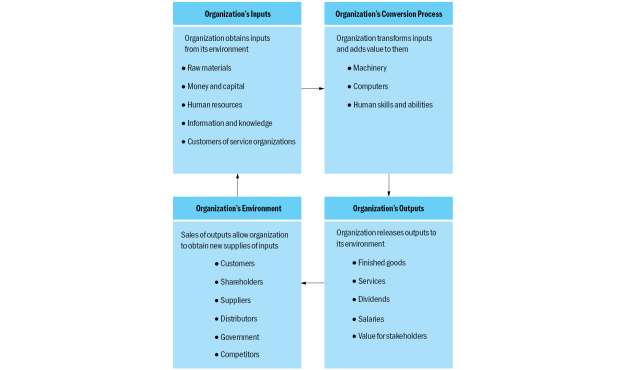
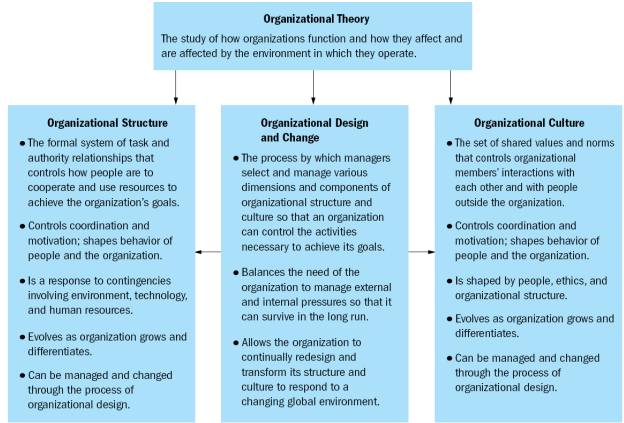
Structural dimensions: Formalization pertains to the amount of written documentation in the organization Specialization is the degree to which organizational tasks are subdivided into separate jobs Hierarchy of authority describes who reports to whom and the span of control for each manager Centralization refers to the hierarchical level that has authority to make a decision Professionalism is the level of formal education and training of employees Personnel ratios refer to the deployment of people to various functions and departments Contextual dimensions Size can be measured for the organization as a whole or for specific components, such as a plant or division Organizational technology refers to the tools, techniques, and actions used to transform inputs into outputs The environment includes all elements outside the boundary of the organization The organization’s goals and strategy define the purpose and competitive techniques that set it apart from other organizations An organization’s culture is the underlying set of key values, beliefs, understandings, and norms shared by employees Performance and effectiveness: Efficiency refers to the amount of resources used to achieve the organization’s goals. It is based on the quantity of raw materials, money, and employees necessary to produce a given level of output. Effectiveness is a broader term, meaning the degree to which an organization achieves its goals. Stakeholder approach integrates diverse organizational activities by looking at various organizational stakeholders and what they want from the organization. A stakeholder is any group within or outside of the organization that has a stake in the organization’s performance. The satisfaction level of each group can be assessed as an indication of the organization’s performance and effectiveness
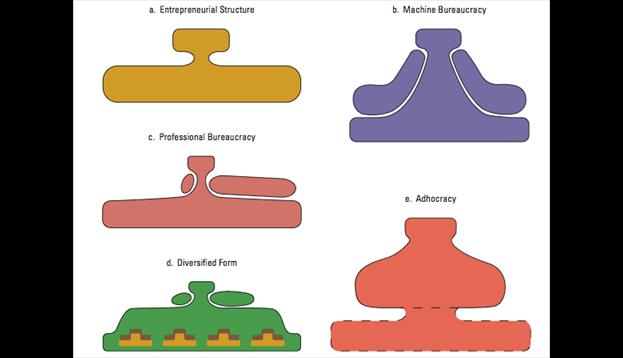
MEINTZBERG’S Typology
Mechanical system design and Mechanistic system design
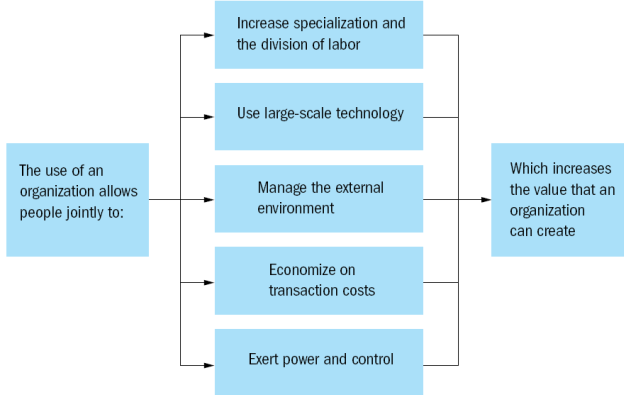
How an organization creates value
Topic 2 ORG STRATEGY AND PUPROSES
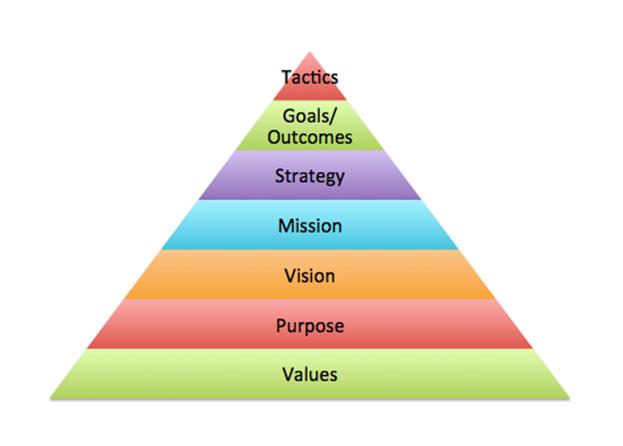
Make sure you can define: An organizational goal is a desired state of affairs that the organization attempts to reach. Strategic intent means that all the organization’s energies and resources are directed toward a focused, unifying, and compelling overall goal. The mission describes the organization’s shared values and beliefs and its reason for being. Competitive advantage refers to what sets the organization apart from others and provides it with a distinctive edge for meeting customer or client needs in the marketplace |
|