|
|
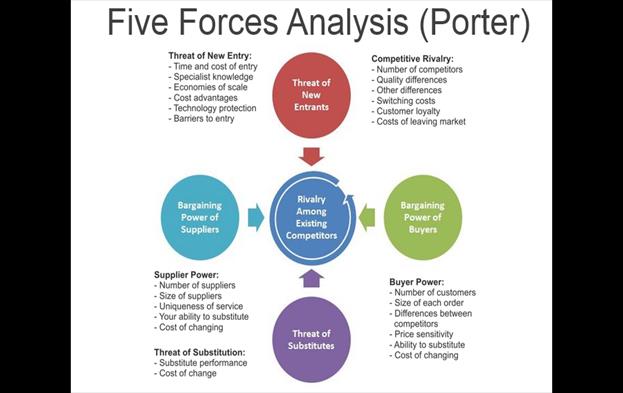
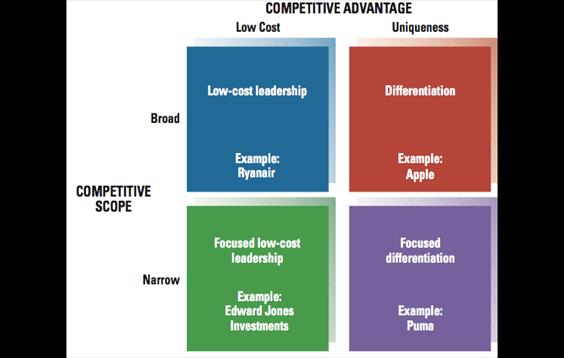
A company’s core competence is something the organization does especially well in comparison to its competitors.Operative goals • performance goals • resource goals • market goals • employee development goals • productivity goals • goals for innovation and change. PORTER
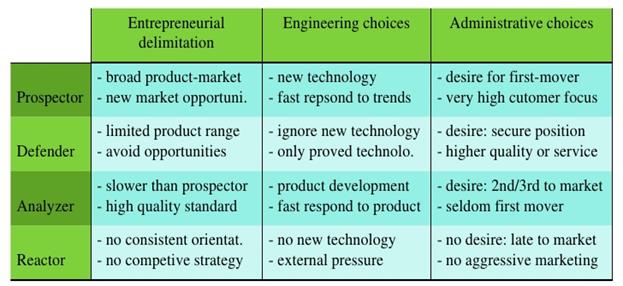
MILES AND SNOW
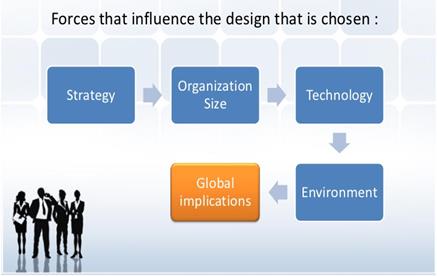
Organizational design
Effectiveness is measured by: • GOAL APPROACH • RESOURCE – BASED APPROACH • INTERNAL PROCESS APPROACH Balanced scorecard
Topic 3 ORG STRUCTURES Self-study, reference materials in the textbook Information-Sharing Perspective on Structure:Vertical Information Sharing • Horizontal Information Sharing Functional, Divisional, and Geographic Designs Matrix Structure Horizontal Structure Virtual Networks and Outsourcing Hybrid Structure Basing on the practical task of changing the type of the structure: Be able to give examples ofmaterial and non-material effects of restructuring, examples of improved behavior.
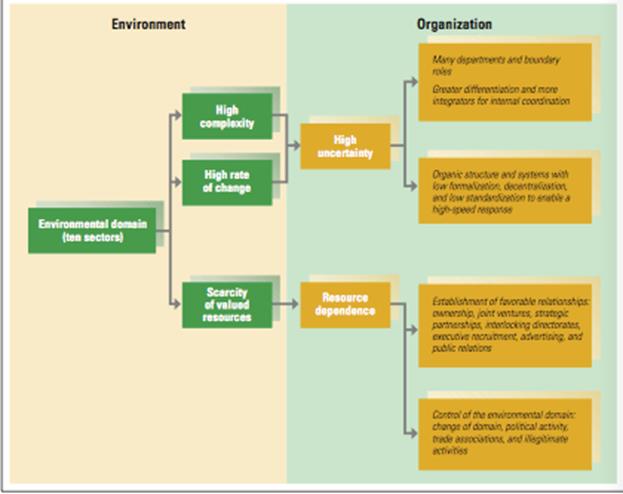
Topic 4 EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Organizational environment is defined as all elements that exist outside the boundary of the organization and have the potential to affect all or part of the organization; Domain defines the organization’s niche and defines those external sectors with which the organization will interact to accomplish its goals; Ten sectors can be analyzed for each organization: industry, raw materials, human resources, financial resources, market, technology, economic conditions, government, sociocultural, and international Task environment includes sectors with which the organization interacts directly and that have a direct impact on the organization’s ability to achieve its goals. The task environment typically includes the industry, raw materials, and market sectors, and perhaps the human resources and international sectors.
A complex environment is one in which the organization interacts with and is influenced by numerous diverse external elements. (aerospace) In a simple environment, the organization interacts with and is influenced by only a few similar external elements (family-owned stores) An environmental domain is stable if it remains the same over a period of months or years. (Public utility) Under unstable conditions, environmental elements shift abruptly. Environmental domains seem to be increasingly unstable for most organizations. (Toy companies)
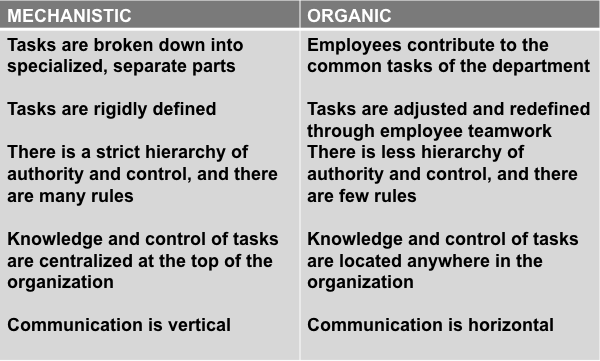
Topic 5 ORG DESIGN AND INTERNAL PROCESSES Differentiationrefers to “the differences in cognitive and emotional orientations among managers in different functional departments, and the difference in formal structure among these departments.” Integrationis the quality of collaboration among departments. ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN Refer to Mechanistic and Organic management models
How environment influences internal processes
|
|